AWS: Cloud Servers
Overview
“The Cloud” is at the core of most internet applications, from distributed data, to servers, to games and web/data hosting services How does it work? How can we leverage it?
Class Outline
Learning Objectives
Students will be able to
Describe and Define
- “The Cloud”
- “Containers”
- Virtual Server “Instances”
- CDNs and scaling horizontally
Execute
Use “Elastic Beanstalk” to Deploy a NodeJS server to an EC2 instance at AWS
This requires 2 parts:
- An “Environment” (container) for our application to run in
- The application code itself to be deployed “into” the environment
Notes
AWS is not free!
- Before you begin your work:
- Become familiar with the Account/Billing pages.
- Setup a cost alert.
- Familiarize yourself with how to turn off any services that you create, use, or start.
We highly recommend that you shut off all services at AWS following the completion of this module
Elastic Beanstalk
Elastic Beanstalk (EB) will automatically wire up essential AWS services to create and deploy a running application.
For Node.js applications, this is generally just going to be an EC2 server instance along with an S3 bucket that stores our files
There are 2 ways to create a new application with EB, detailed below. Either way, all of your environments and applications will be available in the AWS Developer Console (GUI) for you to manage
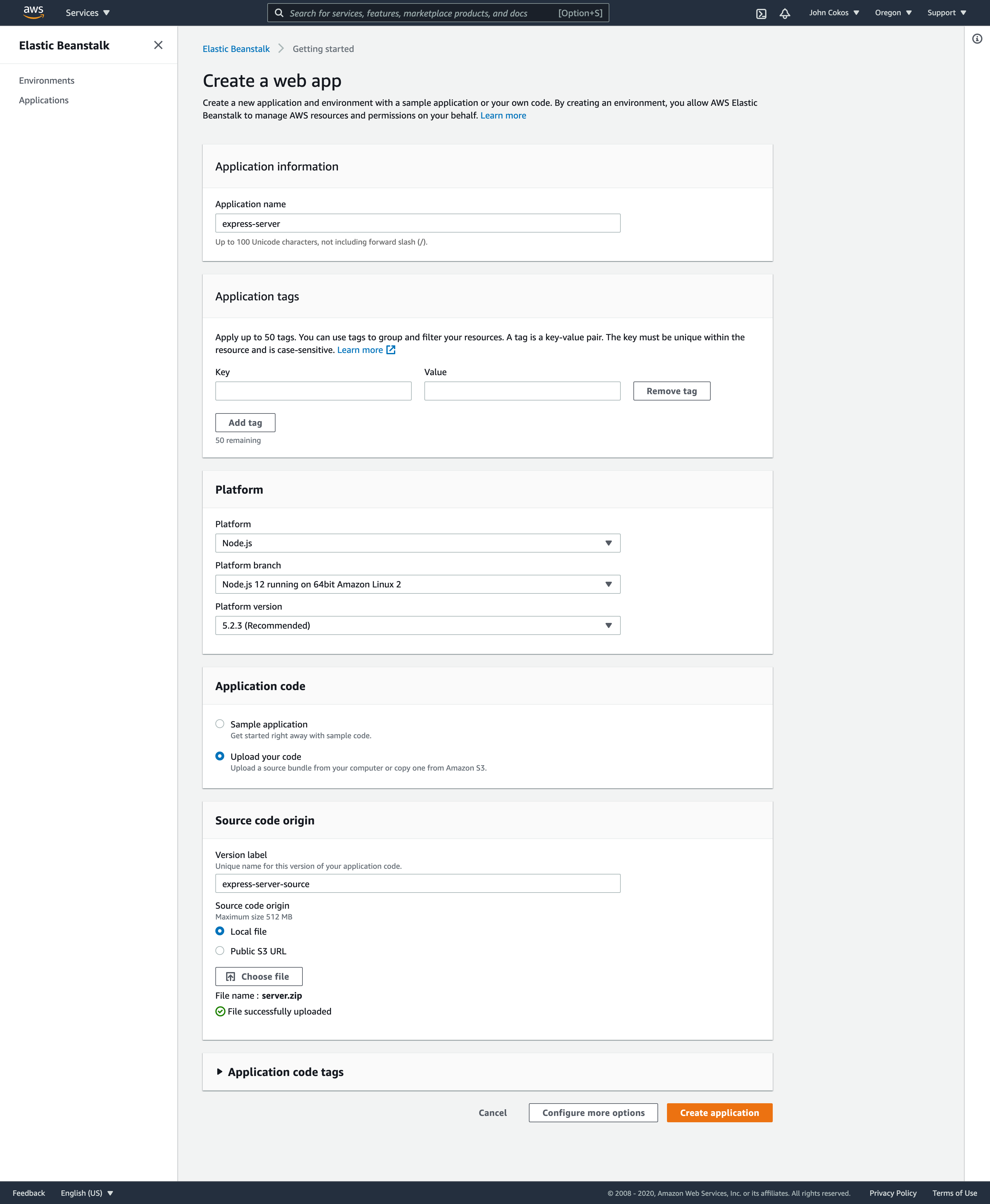
Creating an application with the Elastic Beanstalk GUI
- Choose NodeJS as your platform
- Create and upload a .zip file with your application source code
- Do not include
node_modulesorpackage-lock.json
- Do not include
This will create your application and environment in one step, giving you a full GUI from where you can manage the app
Creating an application using the command line only
First, ensure that you’ve installed the AWS CLI and the aws eb command line utilities.
eb init- Initializes your folder as an Elastic Beanstalk application- Choose your region (
us-west-2) - Choose
[Create new Application]- Note: If you already have an application, you could also choose that to connect
- Answer the other questions as appropriate
- Choose Node.js at the correct version
- Choose your region (
eb create my-environment-name- Create an “environment” for your app to reside ineb deployto deploy your new application to your new environment- You’ll also use this whenever you make code changes
You can then use some other eb commands to manage your apps
eb opento open your app in the browsereb listto get a list of appseb sshto ssh (login) to one of your appseb healthto get a health check on your environments
Auto-Deploy
You can also use GitHub Actions to auto-deploy your source code to your EB Environment whenever you check in your code.
Browse the GitHub Marketplace for actions you can import into your repo. There are many